Reverse Osmosis or RO filter is one of the best water purifiers on the market that provides the safest way to provide pure and clean drinking for residential and commercial use. In Reverse osmosis technology, water is forced to pass through a semi-permeable membrane that leaves behind impurities. These impurities get flushed out from the drain and leave the crystal clear and pure drinking water. To properly understand the objective and procedure of Reverse Osmosis, you need to first understand the process of Osmosis.
Process of Osmosis Explained
Osmosis is one of the naturally occurring processes in nature. In this process, a weaker saline solution migrates to a concentrated saline solution. The molecules of the solution pass via a semi-permeable membrane. One of the best and commonest examples of an Osmosis process is the plant’s root that obtains water via Osmosis process from the soil.
Reverse osmosis can be seen as completely opposite to that of the Osmosis process. Here the molecules are made to pass via a semi-permeable membrane. This membrane results in a less concentrated form of solution. This membrane works like a filter that has very small pores in it that assists in removing the microscopic size of contaminants from the drinking water by way of rinsing them out.
How is the Reverse Osmosis process different from Osmosis process?
In case of an RO or reverse osmosis system of drinking water, the semi-permeable membrane allows water molecules to pass through it while contaminants get accumulated and drained away.
Reverse Osmosis technology is a procedure where in the water gets demineralized or deionized by removing vital minerals from it. This happens when it gets passed under pressure via a semi-permeable RO Membrane.
Where Osmosis is a naturally occurring phenomenon that doesn’t require any energy, in the RO process, you need to supply energy to the water to pass through the RO membrane. This pressure is large as compared to the natural and effortless osmotic pressure. RO method desalinate water, that enables pure water to pass through it while keeping back a vast section of contaminants.
What are the basic parts of an RO water purification system?
Reverse Osmosis method of water filtration is the best and the most popular form of water purification methods available in the present market. Before we start learning about the working of the RO water purification system, it is important to first understand the components present in this filter.
Line valve for cold water:
This is the valve that is connected to the supply line of cold water. This valve acts as the primary water source for an RO system.
Pre-Filter:
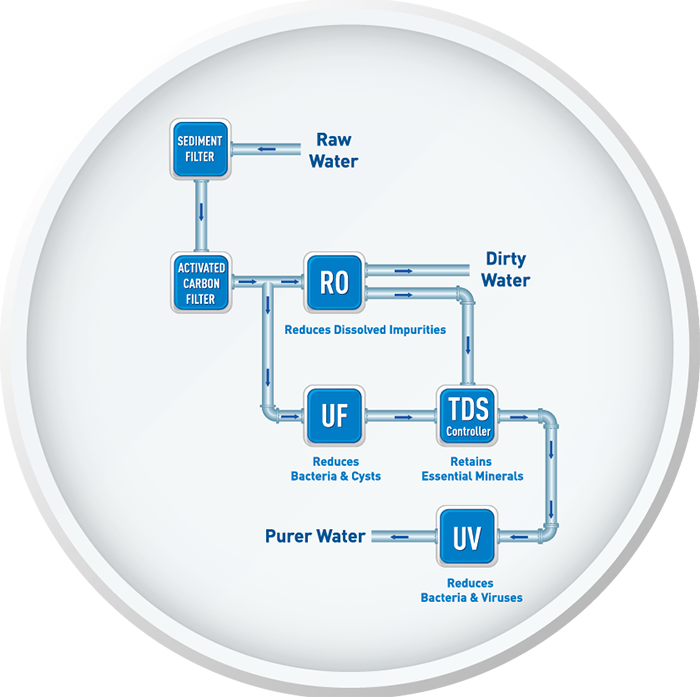
Water that passes through the supply line makes its way to the RO Pre Filter. An RO filter can use more than one pre-filter in its operation. The commonest types of filters that you would find in RO filters on the market are sediment filters and carbon filters.
These pre-filters safeguard the RO membrane from dirt, sand silt, sediment that can block the system. In addition to it, carbon filters can remove chlorine that can result in damage to the RO membrane.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane:
This membrane is the core of the entire filter system. It is a semipermeable membrane that removes a wide range of aesthetic as well as health-related contaminants. When water passes through the membrane, it gets collected in a pressurized storage tank. Here the treated form of water gets stored.
Post-filter:
Water from the RO storage tank goes to the post filter before it goes to the faucet of the filter. The post filter is mainly a carbon filter. Any odor or taste that gets eliminated from the filter via post filter.
Automatic Close Valve:
To save water, an RO system comes with an automatic close valve. This valve closes when the storage tank gets full. This action stops any more amount of water to enter the membrane and clog the water movement to the drain.
Check Valve:
A check valve lies in the exit region of the RO membrane. This valve prevents any backward movement of filtered water from the storage tank of the RO filter. This is helpful as the backward flow of water can damage the RO membrane.
Flow Restrictor:
Water that moves via the RO membrane is monitored by a flow restrictor. Its objective is to maintain the right flow rate as needed to obtain the best quality of drinking water. This restrictor aids in maintaining the right amount of pressure on the entering side of the RO membrane. Flow control mostly lies in the line tubing of the RO drain.
Storage Tank:
The standard form of the storage tank of an RO filter system has the capability to hold from two to four gallons of water. There is a bladder located in the tank that keeps the water pressurized inside the tank when it gets full. A typical Reverse Osmosis tank is 15 inches tall and twelve inches in diameter.
Faucet:
The RO unit makes use of the faucet that is located on the sink of the kitchen. A few areas have got plumbing regulations that require an air gap faucet.
Drain line:
The drain line helps in disposing of the wastewater that contains the contaminants and impurities that have got filtered by the RO membrane.
Four stages of the filter in RO filter

Reverse Osmosis water filtration procedure is a straightforward and simple process. It is a procedure in which dissolved form of inorganic solids like salts gets removed from a water solution.
RO process has the ability to remove upto 99 percent of 65 varying contaminants that includes fluoride, lead, chloramine, pesticides, chlorine, detergents, nitrates and sulfates, dissolved salts, and more. Most of the RO units includes a four or stage procedure for optimal quality of water.
Sediment filter:
This stage of water filtration is made to strain out silt, dirt, and sediment. It is especially beneficial as this filter safeguards dirt from entering inside the delicate reverse osmosis membrane that can cause wear and tear due to the presence of sediment.
Carbon filter:
This filter works by eliminating chlorine and other types of contaminants that impact the lifespan and performance of the RO membrane. It also helps in improving the odor and taste of the water.
Reverse osmosis membrane:
The RO membrane is semipermeable in nature. It is made to permit water through it but eliminates almost all types of additional contaminants.
Polising filter:
In the 4 stage RO System, a carbon filter will work by polishing the water to eliminate any taste and/or odor that have got remained after passing through all the above filters in the system. So, by the end of this filter, you can ensure that you get an outstanding level of drinking water.
Steps of water filtration in RO water purification system

Step 1: Pre-filtration
The first and foremost step in water purification with reverse osmosis methodology is to safeguard the membrane. Pre-filtration method assists in removing larger sediment that includes dissolved solids, and aids in lowering the levels of chlorine.
Reverse osmosis or RO technique works remarkably. It starts off with good quality water and processes it to make it incredibly safe and delicious to drink. It is advisable not to use an RO system with hard water that is more than 10 grains/ gallon.
If you find that the water is very hard, then you need to begin with a water softener. Use it first before you use an RO filtration system. This is very important as the scale that can build-up from the hardness of water can easily damage the system. Thus, to protect your RO filtration system, soften the water first before you pass it to an RO water purification system.
Step 2: The RO or Reverse Osmosis Membrane
After pre-filtration, water reaches to the main unit of the RO system. Here, the water is forced via the semi-permeable RO membrane under pressure. This membrane is made up of a synthetic form of plastic material that enables water molecules to pass through it while restricting certain elements such as chlorine, calcium, sodium, and large sized molecules such as urea, glucose, viruses, and bacteria.
RO drinking water systems available in today’s market are certified as well as tested for the elimination of:
- lead
- copper
- arsenic
- nitrates,
- nitrites
- chromium
- fluoride
- selenium
- barium
- radium
- cadmium
- cyst, and
- total dissolved solids (TDS)
Steps 3: Post Filtration
Before the water becomes purely safe and palatable to drink, it passes through a 2nd carbon filter that eliminates any type of contaminants that could have passed the RO membrane and made their way till this stage. Now, the water gets filled in the storage tank from here it waits till it is ready to be used.
Steps 4: Final Polish
The final filter is the “in-line carbon filter”, that gives the last polish to the water as it comes out from the faucet. It is used to eliminate odor or flavor that may get into the holding tank.
Conclusion
Reverse Osmosis water purification system proves to be a proven and effective technology to generate water that is appropriate for most of the industrial applications that need deionized or demineralized water. An RO system makes a perfect water filtration solution for most homes.
Water purification is the most valuable equipment that has become one of the most essential needs of any house. The power of RO water purification system lies in the four stages of the filtration process. Making a better investment in RO purification systems helps you save money, and safeguard environment in the longer run. With the right design of the system, maintenance program, as well as experienced service assistance, an RO system provides several years of high quality and purity water.